Scholar Inbox: Daily Research Recommendations just for You

How AI Affects Our Everyday Lives

“AI and Freedom” citizens’ council: encouraging the public to participate
Article Overview
Scholar Inbox: Daily Research Recommendations just for You

How AI Affects Our Everyday Lives

“AI and Freedom” citizens’ council: encouraging the public to participate

How a tiny animal helps us improve brain simulations with AI
A network for women to support each other

Human-guided Neural Networks for Synchrotron Experiments
Knowledge Tracing for Life-long Personalized Learning
Navigating 20 Million Papers at Once to Uncover Knowledge

Better Understanding the Monsoons and the El Niño

How to put on an exhibition

Do humans and algorithms learn alike?
New Directions in Science Communication: The Themed Channel “AI and Sustainability”

Making the world a little bit better with AI

How to make business trips more climate friendly

Developing Data Science and Machine Learning in Africa

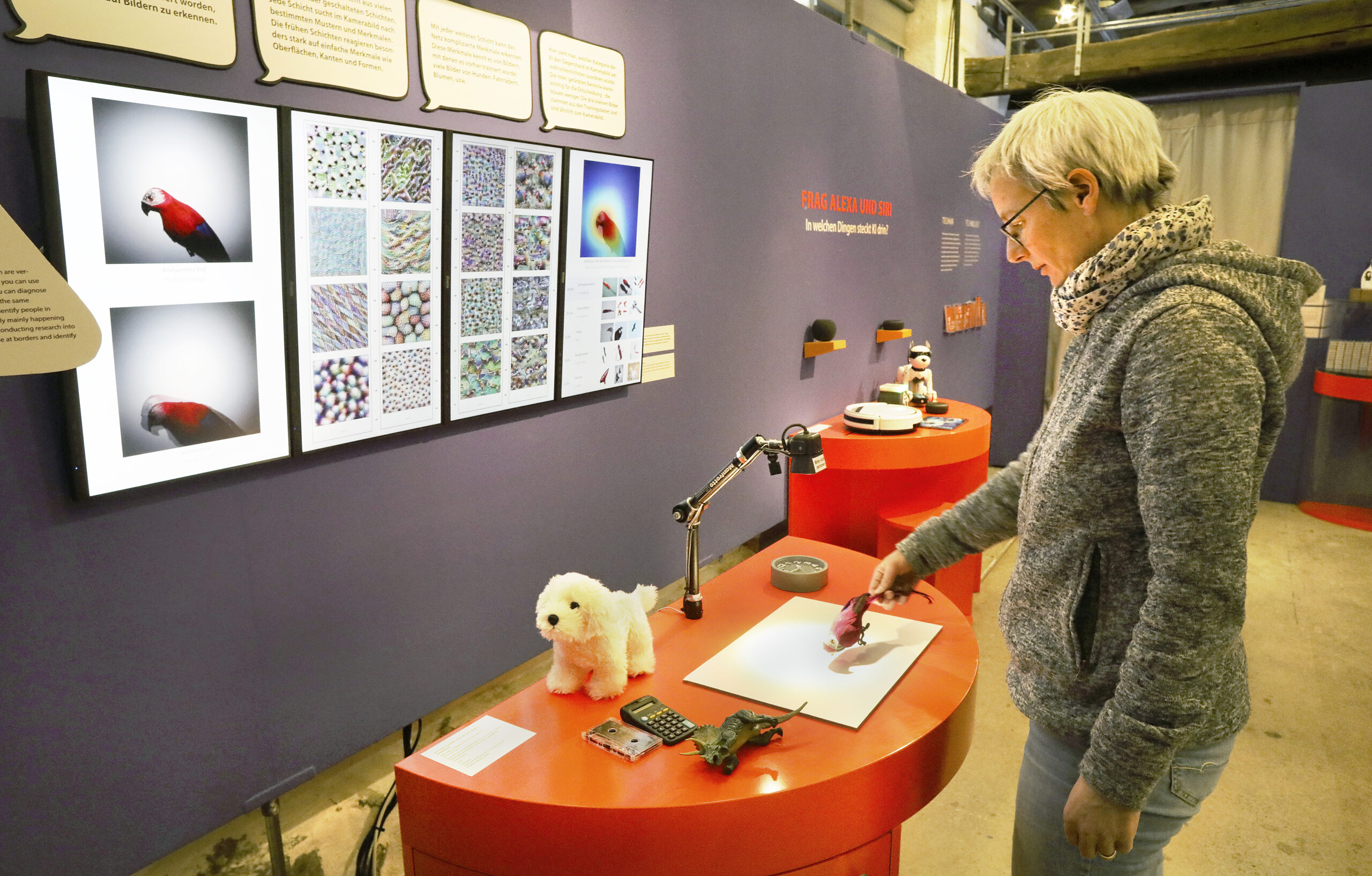
Opening the Black-Box of Deep Learning in Image Classification
Escaping Plato’s Cave: Teaching machines the 3D nature of our world

Predicting future energy supply

Rooting Democracy in the Digital Age

Artificial Intelligence (AI) – Should it explain itself?

Fusing Physical Knowledge with Neural Networks’ Flexibility

From Cape Town and Khartoum to Tübingen
Do machines see like humans? They are getting closer

Machine Learning Decodes Tremors of the Universe

AI as Mediator

Towards AI systems that can explain decisions

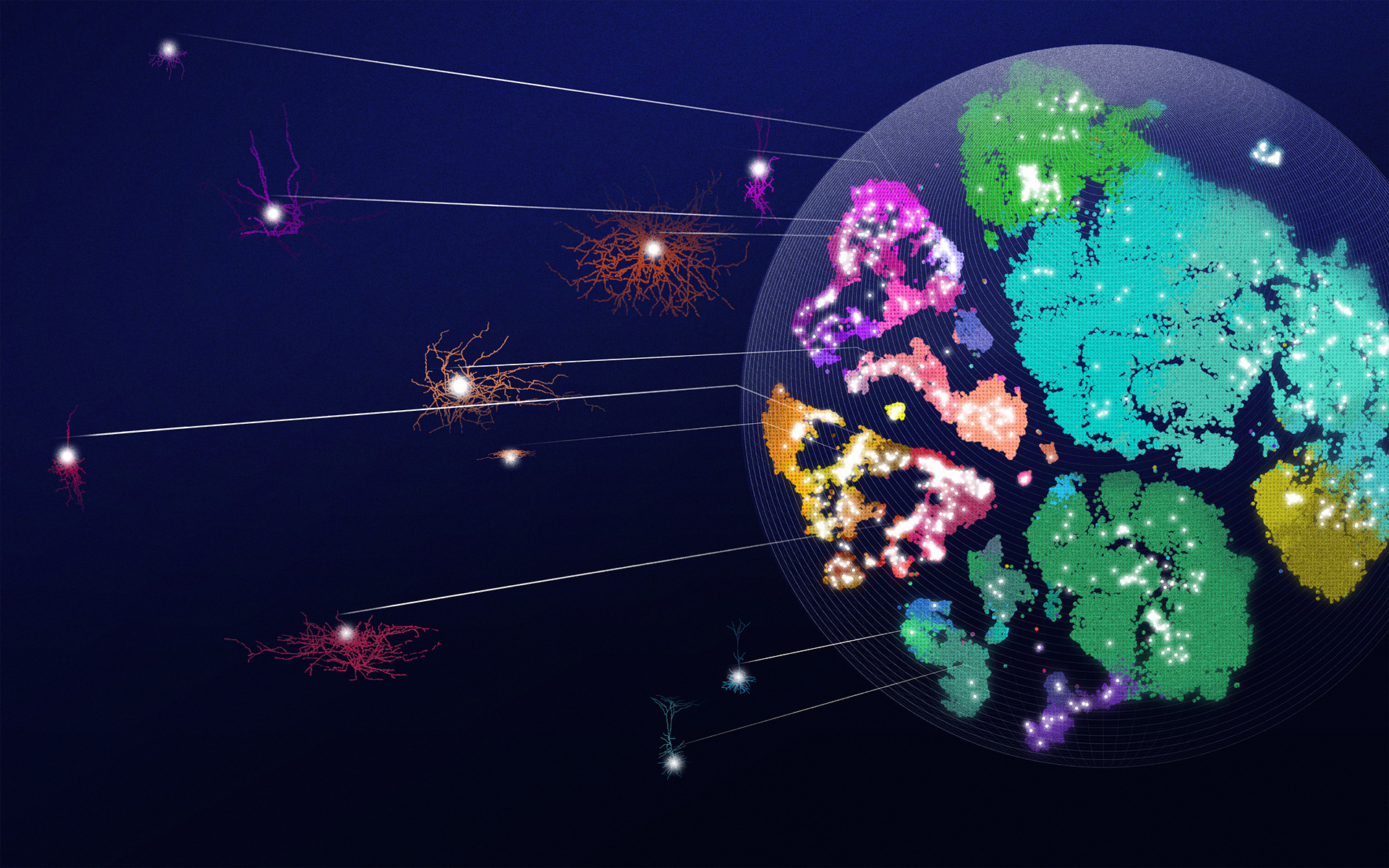
First comprehensive atlas of neuron types in the brain
Machine Learning Improves
Super-resolution Microscopy
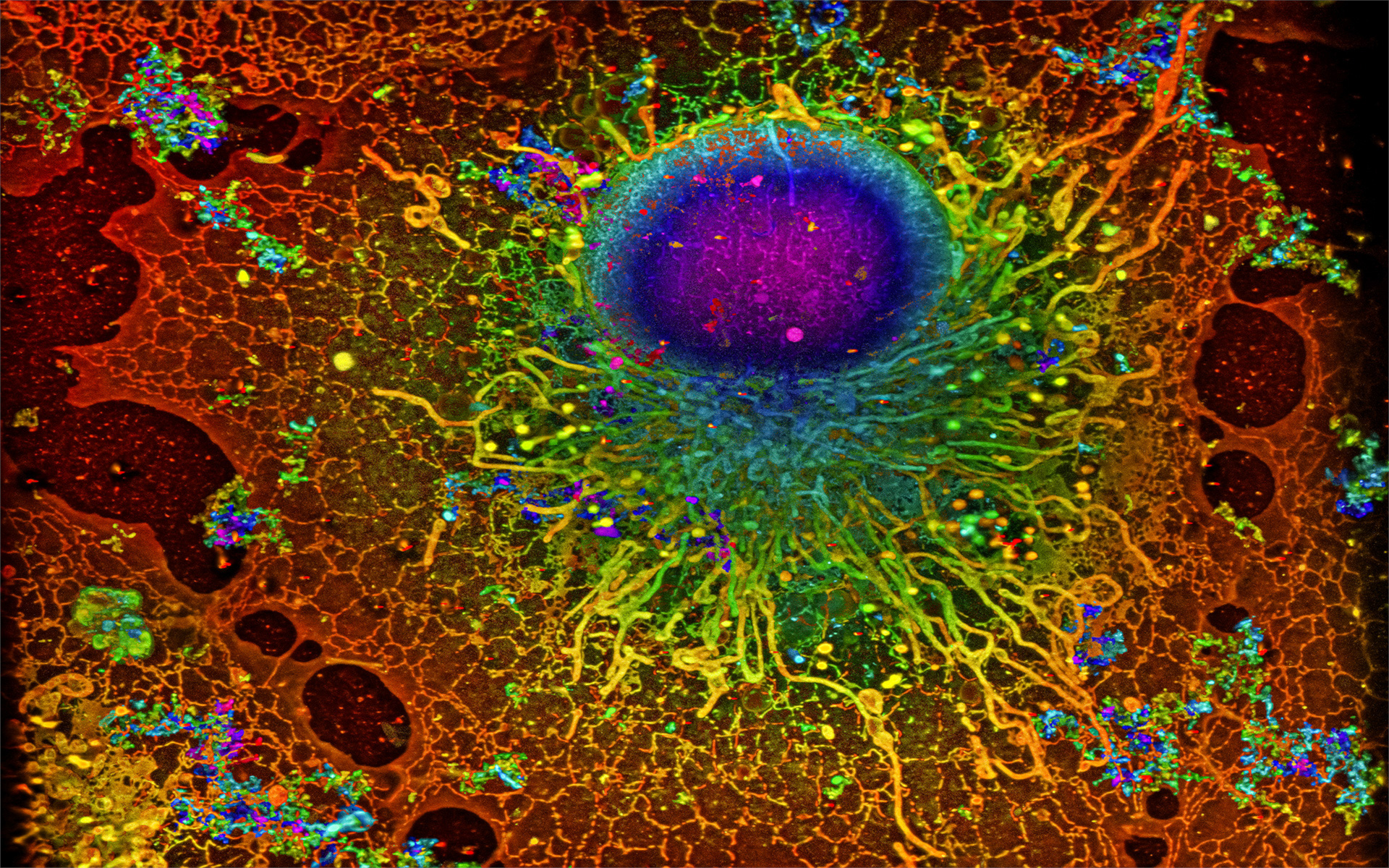
Identifying Models in
Neuroscience with Machine Learning
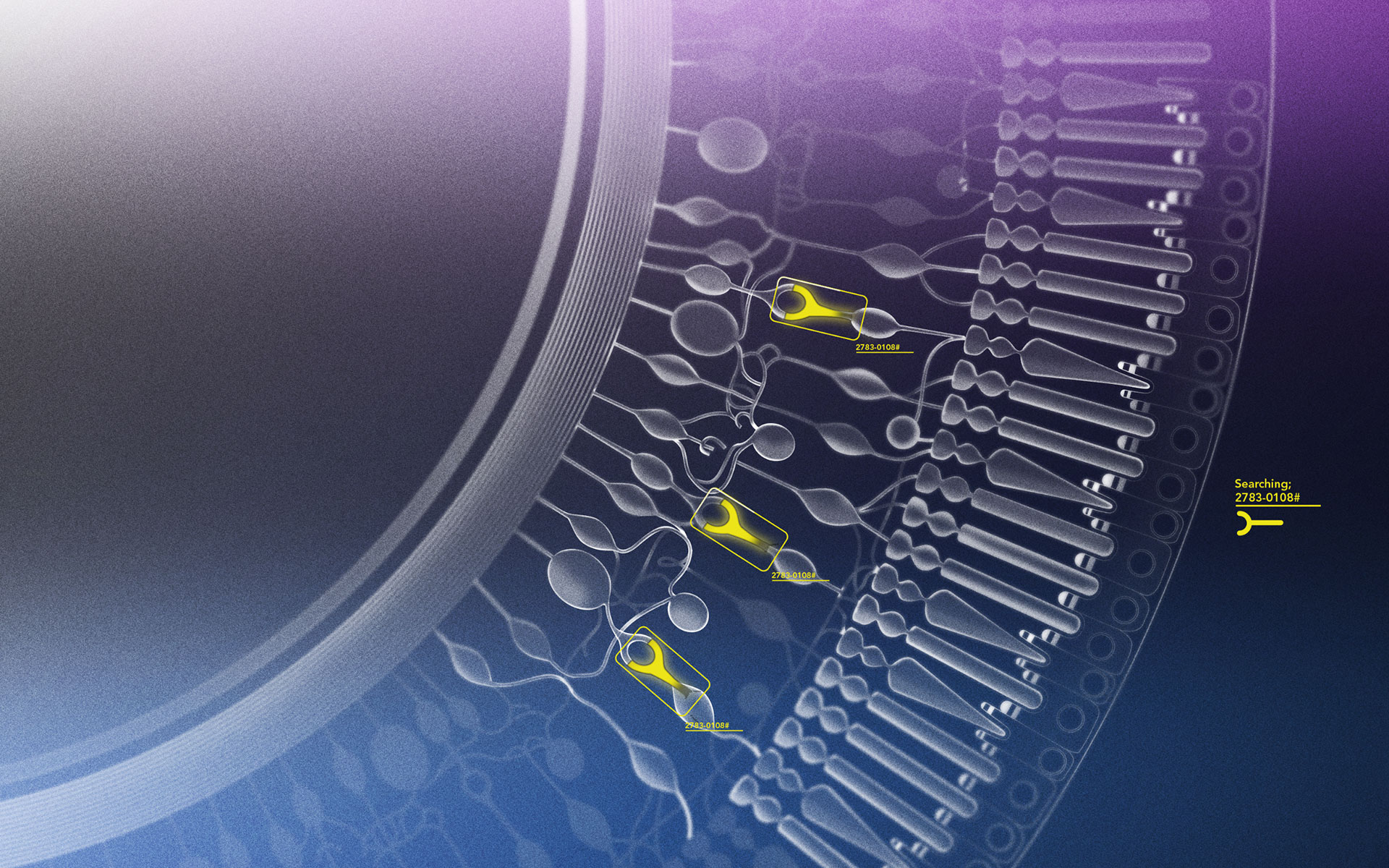
Where Algorithms and People Are Allies

When Artificial Intelligence Predicts a Heart Attack

Responsibility Cannot Be Delegated to an Algorithm

Using Machine Learning for 3D Soil Mapping

Painless Uncertainty for Deep Learning